Table of Contents
What is Dynamic Cone Penetrometer?
Dynamic Cone Penetrometer(DCP), is a device used to measure the intensity of the on-site soils. It also helps track the state of granular layers and over time subgrade the soils in pavement parts. It can be used to decide the right solutions for the sites, particularly if involving soft soils.
This is often used where it is appropriate to assess the CBR importance of compacted soil subgrade below current road pavement. Continuous measurements may be taken down to a depth of 800 mm or to a depth of up to 1200 mm where an extension rod is mounted.
The DCP is an instrument which is simple and compact. It consists of a reinforced conical end, a large diameter steel tube, and a regular weight hammer (8 kg), which is thrown into an anvil from the top of the pole to advance the end through the ground.
What is the principle of the working of DCP?
It consists of a reinforced conical end, a large diameter steel tube, and a regular weight hammer (8 kg), which is thrown into an anvil from the top of the pole to advance the end through the ground.
Describe the working procedure of DCP in brief?
The DCP is an instrument which is simple and compact. It consists of a reinforced conical end, a large diameter steel tube, and a regular weight hammer (8 kg), which is thrown into an anvil from the top of the pole to advance the end through the ground.
Applications of Dynamic Cone Penetrometer
- Soil knowledge is always restricted and is mostly obtained from beyond the limits of the base field, but anywhere else on the site we can need to determine the soils.
- Information may be collected about the variability of soil intensity with depth, which can be crucial to the production of the best remedy for unsuitable subgrade soils.
- One can gather information fairly quickly from a number of locations, and you can see how the soil conditions differ around the site and react accordingly. One gets detailed and reliable knowledge regarding the soil conditions in the field and at the time of development.
Apparatus for Dynamic Cone Penetrometer
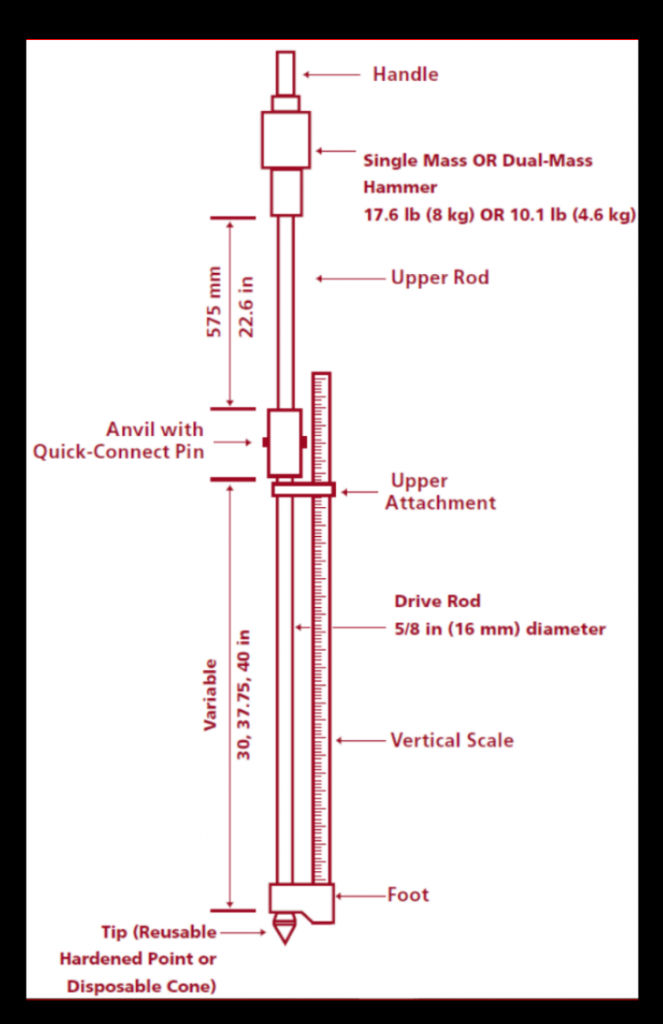
- Handle
- Top Rod
- Handguard Cursor
- Bottom Rod
- 1m rule
- 60 degree Cone
- Hammer(8kg)
- Anvil
- Handguard Cursor
- Bottom Rod
- 1m rule
- 60 degree Cone
- Tommy bars and spanners
Dynamic Cone Penetrometer
- Handle rod
- Anvil rod
- Bottom rod
The hammer is raised up to the top of the rod and released to push the rod into the wall. The penetration (in inches or millimeters) is measured after the hammer blows with the aid of the embedded vertical scale.
For More Details: Civil engineering
Correlations have been developed between measurements with California Bearing Ratio (CBR) and DCP so that the result can be interpreted and contrasted with pavement architecture CBR requirements.
Procedure for Dynamic Cone Penetrometer
- After the setup of the instrument, the device’s zero reading is recorded. It is achieved by putting the DCP on a hard surface, maintaining its verticality, and then noting down the zero reading on the proforma in the correct position.
- When the check is complete, DCP is withdrawn by softly pressing the weight against the handle upwards. It will be handled with care, as though the instrument’s life were being shortened aggressively.
- The tool is kept straight, and the weight is added to the handle with caution. Until it’s permitted to drop, the weight shouldn’t hit the handle, and the operator should let it drop naturally and not lower it with his hands.
- It is best to take a test at penetration intervals of around 10 mm. Normally, though, getting a reading of a meter after a specified amount of blows is better.
- Therefore, it is appropriate to adjust the number of blows between readings according to the intensity of penetration of the sheet. For high-quality granular bases, readings are usually acceptable after every 5 or 10 blows but readings after every 1 or 2 blows can be sufficient for poorer sub-base layers and sub-grades.
Dynamic Cone Penetration (DCP) testing is used to measure the strength of the soil and the thickness and location of subsurface soil layers. The Dynamic Cone Penetrometer is the tool used to determine underlying soil strength. In this article, we’ve covered the procedure involved and applications of DCP. Hope this article helped you.



