Bulking of Sand is small grains of silica (SiO2) formed by the decomposition of rocks. It is one of the most important construction materials. It is broadly used in concrete, cement mortar, lime mortar, earth filling, etc.
What is the Bulking of Sand?
The rise in sand density due to increased moisture content is referred to as sand bulking. A layer of water is produced around the particles of the sand which causes the particles to take one side from each other and thereby increase the volume.
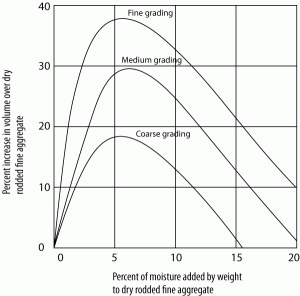
The rise in sand humidity raises sand density. The rise in density of dry sand, or rain, is known as bulking. Sand bulking depends on the amount of humidity in the sand and the particle size as well. Five to eight percent of the increase in sand moisture can increase sand volume by up to 20-40%. Also, the finer the sand is, the greater the density will be, and the higher the amount for the coarser sand will be comparatively less.
Sand relies on the sand’s humidity. But when the temperature is raised by introducing more heat, the sand particles are pressed next to each other as the film around the sand particles cracks and the sand bulking is decreased. Dry sand and the water-filled sending will have the same size. This definition is used to evaluate the amount of sand bulking in the test.
Bulking of Sand Significance
Simplified, it can be said that sand bulking is literally the uncompacted looseness of sediment. Water usually reduces the pores in the sand and compacts the dust.
For construction, sand is used to minimize separation and to fill the gaps between cement and rough aggregates. We require 1 m3 of concrete salt, for example, we need to learn the approximate value of sand bulkage. If the given specimen has a 25% bulkage then we need to take 25% more sand or 1.25 times more sand when batching volume to get 1 m3 of concrete sand. Read More
Because of the bulkage cost, if we don’t take this extra amount of sand, the total volume will be decreased to 75% by adding water. We recognize that the value of concrete is highly dependent on the material being correctly proportioned. Generally speaking, we find the wet density of cement to be 1.5 times the amount of dry concrete, in this situation we usually use about 30% of sand bulk and 20% of waste. If we do not find the sand mass, the maximum volume will be decreased and the overall quality of cement will be impacted.
Test Procedure:
Following measures, the percentage of sand bulking in a given sample can be measured
- Fill the specimen with the weighing tube up to 200 ml level.
- Steel scale can be used for accurate measurement, but sand compaction is not allowed.
- Removal of the sand to a bowl.
- 100ml of liquid refills the weighing tank.
Bulking of Sand=(200−a/a)×100
- The process should be repeated twice, and the average tree observation value for the given sample will be the percentage of sand bulking.






