
Raft foundation is actually a thick reinforced concrete slab resting on a large area of soil reinforced with steel supporting columns or walls and transfer loads from the superstructure to the soil. A large single slab that supports the structure as a whole is called a raft. Raft & piled raft foundation is used to distribute structural loads when the bearing capacity of the underlying soil is low.
A slab can cover the entire bottom area of the building or several smaller ones can be strategically placed below pillars or walls (Hansbo, 1989). A single raft is preferable in order to reduce differential settlements or when there are local parts of the soil where the strength deviates. The raft can have an even thickness or have stiffer parts where structural loads from walls or pillars are transmitted.
It can be designed with a stiffness large enough for the contact pressures to be assumed equally distributed throughout the plate. Otherwise, the distribution will depend on the relative stiffness between plate and soil.
Table of Contents
Advantages:
- Raft foundation is constructed for shallow depths hence, it requires less excavation.
- Mat foundations are used where the bearing capacity of the soil is less.
- Mat foundations distribute the loads coming from the superstructure over a large area.
- Using the Raft foundation the differential settlement of the soil is reduced.
Disadvantages:
- In the construction of the raft foundation, the reinforcement requires a larger amount which increases the project cost.
- Skilled laborers are required in the construction of the Raft foundation.
- In the construction of the raft foundation, special care should be taken in the case of point loads.
Piled Raft Foundation
To carry the excessive loads that come from the superstructures like high-rise buildings, bridges, power plants, or other civil structures and to prevent excessive settlements, piled foundations have been developed and widely used in recent decades. However, it is observed that the design of foundations considering only the pile or raft is not a feasible solution because of the load sharing mechanism of the pile-raft-soil.
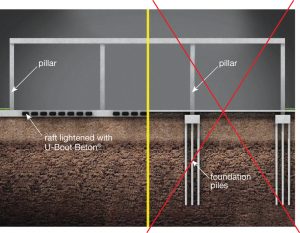
Therefore, the combination of two separate systems, namely “Piled Raft Foundations” has been developed (Clancy and Randolph (1993)). The Raft & piled raft foundation system is verified to be an economical foundation type comparing the conventional piled foundations, where, only the piles are used for reducing both total and differential settlements, and the contribution of the raft is generally disregarded. Piled raft foundations are used mostly for large structures and in situations, where the soil bearing capacity is less and the soil is unsuitable to prevent excessive settlement. Read More
The load-settlement behavior for different design approaches, concerning a piled raft, is presented in Figure. Curve 0 represents the behavior of a raft acting alone. Curve 1 represents the conventional design approach. Curve 2 illustrates the “creep pile principle”, in which the piles are designed with a lower factor of safety. Curve 3 represents the use of full utilization of the piles at the design load, by strategically placing the piles as settlement reducers. The reduction in the number of piles for curves 2 and 3, results in a larger amount of the load carried by the raft. Fewer piles result in a more economical design (Poulos, 2001). Read more about the Pile foundation
Factors affecting the Behavior of Piled Raft Foundation
Many researchers have examined the behavior of piled rafts. The following factors can be listed as the main determinants of the behavior:
- The number of piles,
- Length of piles,
- The diameter of piles,
- Pile spacing ratio,
- Location of piles,
- Stiffness of piles,
- Distribution of load,
- Level of load,
- Raft thickness,
- Raft dimensions,
- Type and stiffness of the soil.
This article gives information about the Raft & Piled Raft foundation, its advantages, disadvantages, and factors affecting the behavior of the Piled Raft foundation.
