
Table of Contents
What is the RCC Foundation?
The foundation is one of the most important components of the structure. Foundation is described as that part of the structure which transfers the load from the structure as well as its own weight over a large area of soil in such a way that the load does not exceed the soil’s ultimate bearing ability and remains within a tolerable limit of the total structure settlement. The base is the portion of a house on which the structure sits. The firm earth on which the floor lies is regarded as the base layer.
Need for a Foundation
The Foundation will meet the following goals:
- To disperse the structure’s weight over a wide area of land.
- Stop the system from traveling laterally.
- Improve the integrity of the systems.
- Stop unfair arbitration.
Different types of foundation
As we know, different types of soil occur and soil bearing potential is specific for each particular soil type. Thus, depending on the structure’s soil profile, size, and load, engineers have chosen different foundation types.
Types of Foundation
Both foundations are typically classified into two groups, such as Shallow Foundations and Deep Foundations. The terms Shallow Foundation and Deep Foundation apply to the density of the foundation’s soil. Generally, if the foundation width is larger than the foundation depth it is known as “Shallow Foundation” and if the foundation width is less than the foundation depth it is named “Deep Foundation.” Furthermore, shallow and deep foundations can be further graded as shown in the accompanying table.
System
- Deep Foundation
- Shallow Foundation
Deep Foundation
- Pile
- Pier
- Caisson
Shallow Foundation
- Isolated Spread Footing
- Wall Footing
- Combined Footing
- Cantilever Footing
- Raft Foundation
Deep Foundations
Various Types of Deep Foundations are listed below:
1. Pile Foundation

Pile Foundation of Building
The base of the Pile is a common type of deep foundation. They are used to reduce costs and it is beneficial to transfer loads to soil strata that are beyond the scope of shallow foundations, as per considerations of soil quality. Pile is a slim member relative to its weight, with a small cross-sectional region. When the bearing capacity of soil near the surface is relatively low, it is used to transmit foundation loads to a deeper soil or rock strata. Pile transmits load either through rubbing of the clothing or through a bearing. Pile foundations become economic while Soil with large bearing potential is at a greater depth, utilizing a pile base. Read More
- If possibilities of irrigation canals being constructed in the nearby area occur.
- When a strongly focused charge is placed on the base.
- When the supply of raft or grillage foundations is very costly.
- In secluded places.
- When in fact the coating of the topsoil is compressible.
2. Pier Foundation
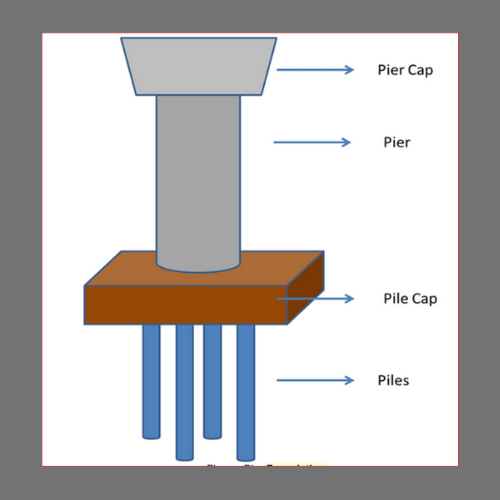
Pier foundation
Pier is an artificial device that conveys heavier load that can not be conveyed via shallow foundations. It is typically shallower than the base of a hill. Pier foundation is a cylindrical structural component which transfers heavy load by end bearing from superstructure to soil. Unlike plate, it can move load only through bearing, and not through skin friction. The Pier Base becomes economical when:
- Sound rock strata are located at the surface under a decomposed rock sheet.
- The topsoil is hard clay that is immune to carrying pile driving.
3. Caisson Foundation

Caisson Foundation
Caisson base is a watertight reinforcing framework that is used as a bridge deck, dam construction, etc. It is typically used in systems that need a base underneath a river or related bodies of water. The justification for choosing the caisson base is that it can float to the desired location and then fall into place. Caisson Base is a ready-made hollow cylinder sunk into the soil to the degree required and then lined with concrete that eventually transforms into a base. It is mostly used as piers for bridges. Caissons are prone to construction practices and lack structural experience.
Types of caisson foundation such as:
- Box Caissons
- Open Caissons
- Floating Caissons
- Sheeted Caissons
- Excavated Caissons
- Pneumatic Caissons
Shallow Foundations
Various types of shallow foundations are discussed below:
1. Isolated Footing

Isolated Footing
This is the most common and cheapest foundation form since this is the most economical foundation style. They are commonly used for ordinary usually up to five stories houses. Isolated footing type foundation consists of footing at the base of the column. This type of foundation is independent footings. Usually, each column has its own footing. The footing directly transfers the loads from the column to the soil. The footings may be rectangular, square, or circular in shape. The footing size can be measured approximately by dividing the total load at the base of the column by the soil’s acceptable bearing power.
- Isolated Spread Footing is cost-effective when: system load is relatively low.
- Columns are not mounted at close range.
- Soil carrying potential is strong at a shallow depth.
2. Wall Footing

Wall Footing
Its form of footing is used for the delivery to the ground of loads from longitudinal load-bearing walls. The base of the Building extends along with the building. The ground base thickness is normally 2-3 times that of the building diameter. The foundation of the wall is a continuous line of slabs along the wall. The building of wall frames is used with mortar, cement, reinforced concrete, etc.
- Loads to be transferred are of low size, wall foundation is economical.
- The footing is built on thick gravel and sand.
3. Combined Footing
The combined base is very close to the isolated structure. When the framework columns are positioned in close proximity, or the soil’s bearing ability is poor and their footing overlaps one another, a combined foundation is given. Combined footings are called the foundations which are rendered specific to more than one board. These can be in type triangular, tee-shaped, or trapezoidal. The main aim is the consistent distribution of loads across the entire footing region. For this, the center of gravity of the footing field will correspond with the center of gravity of the overall loads.
- On one side of the footing, lengths are reduced to some lower value.
- The columns are placed close to each other, the resulting foundations are physical.
- When the column becomes close to the line of the land, and the separated feet cross the line of the property or becomes excentric.
4. Cantilever
Strap footings are identical to combined footings and it is equivalent to the combined footing to accept or choose strap footing. The footings underneath the columns are individually built-in strap footing and attached by a strap plate. In general, when the edge of the footing can not be reached beyond the line of the house, the exterior footing is attached to the internal footing by strap support.
5. Raft Foundation
Raft or Mat foundations are used in situations where other shallow foundations or pile foundations are not sufficient. It is also advised in cases where the soil’s bearing ability is low, the strain of the system is to be spread over a large area, or where the structure is continuously subject to shocks or jerks. Raft Base consists of a reinforced concrete slab or T-beam slab that is mounted over the entire structural area. The whole basement floor slab serves as the backbone in this form of structure. The structure’s total load is spread evenly across the entire structure region. This is named Raft because the structure seems to be like a canoe floating on a sea of water in this situation. Rafting is an economic foundation when: the land is low and the load has to be distributed over a large area. Read More about Raft Foundation
- The floor is built of a cellar.
- Most kinds of bases are not feasible.
- Differential arbitration will be halted
- Columns are placed at close length.
In conclusion, the foundation is a supporting structural component that transfers the total load from a slab, pillar, column, wall, etc. The foundation’s main objective is to provide support to the overall structure.
