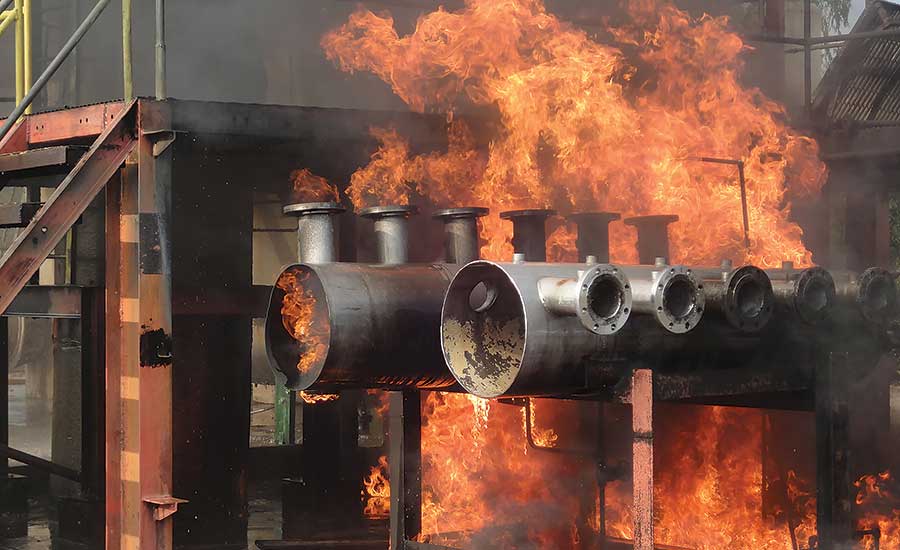
Fire protection has been a big concern in the structural design of buildings for a very long time and it has become an integral part of all forms in construction works today. Fire breakouts can be abrupt and harm not only the building and valuable properties but also threaten the lives of the inhabitants.
But with the increasing knowledge of fire protection, engineers and architects have succeeded in developing methods and structures to ensure maximum protection in the event of fire incidents.
Specific Fire Safety strategy
The very first step in fire-resistant construction, of course, is optimizing the use of non-combustible materials. Many Indian Standard (IS) codes provide guidelines on safety procedures and the use of fire-resistant materials at building sites. A building is a mixture of different fundamental components. To render a building fireproof or fire-resistant, it is important to ensure that certain elements remain unaffected by the fire effect.
Load-bearing walls: The load-bearing walls along with the base form an integral part of every structure. Such walls are responsible for the movement of vertical loads from slabs and beams to other suitable members of the structure and eventually to the base. Such walls would also have a particular thickness to withstand the fire impact. In a segment, they should be thicker to serve for a significant time as fire barriers. You can get the exact segment thickness from IS code- 1642 (1989).
Flooring: The flooring materials are mostly made of bricks, concrete, stones, tiles, etc. because they are considered a part of fire-resistant construction. Nevertheless, where the use of these materials is not feasible, it is appropriate to use wood floors or other floors that are more vulnerable to fire. Thicker joists can be used for the building of wooden floors. Such joists should also be put away at a greater distance. Additionally, insulators may also have protective coverings on the flooring. This may involve materials such as bricks and ceramic tiles.
Framed Structures: There may be two types of framed structures, concrete reinforced, and steel structures. Stainless steel structures tend to twist and bend under heavy fire. Then they are given a metal lath or plaster protective coating. Bricks, concrete, or tiles can also, be used and should have a minimum thickness of 10 cm. In the case of reinforced concrete, the frame members beams and columns should be provided with an adequate concrete cover to ensure optimum fire efficiency. This cover should have a thickness of at least 5 cm.
Partition walls: In the construction of fire-resistant partition walls, Reinforced Cement Concrete (R.C.C), Reinforced Brick Concrete (R.B.C), Asbestos cement board, hollow concrete, etc. are typically used. They are however linked with metal lath and plaster when wooden partition walls are built.
Ceiling: Asbestos cement sheet, metal lath, and plaster are also used to improve the fire-resistance in the ceiling frame. Of greater stability and strength, the ceiling and floor joists often have to be directly connected.
Doors: In the case of a fire emergency, the doors and windows serve as the exit points and so it is very important to maintain their integrity during construction. They have to be glazed and fitted with reinforced glass panels, as they have a higher thermal resistance than usual glass panels. The use of metal door frames is also a step towards guaranteeing fire protection.
Stairs: In case of a fire, windows and doors provide sufficient escape routes for single-story or two-story buildings. But the position of the staircase is important in the case of multistorey buildings. It should be equally accessible from different points inside the house. As for the stuff, it is advisable to use R.C.C. for staircase construction. For further protection, enclosure walls made up of fire-resistant materials should also be built around the staircase hall.
Read More:Civlengineer-online.com
Roofs: From the fire protection standpoint, a flat roof is always safer. That is because in case of adverse wind conditions fire spreads faster on a sloped surface. If the construction of a sloped roof is necessary, however, the ceilings should be built or coated with fire-resistant materials.
What are the constituents of fire-resistant mortar?
Fire-resistant mortar is used to plaster walls of all forms, such as bearing walls, non-bearing walls, and partitions. Doing so enhances every structure’s fire-resistivity to a certain degree. Calcium alumina cement is the principal constituent imparting its properties to fire-resistant mortar.
This cement is then mixed in the appropriate ratio with sand, fire clay, and water, and fire-resistant mortar is thus made. Fire clay is a ceramic clay type that has resistivity to extremely high temperatures. Of this purpose, they are used in homes, furnaces, and professional kitchens of fire-resistant linings and mortar.
What is an asbestos cement board?
Asbestos cement board is also known as an insulating board for asbestos. Asbestos occurs naturally, and blends with cement readily. Adding asbestos to cement makes it longer lasting and heat resistant, rendering the cement board fireproof. Therefore, it is clear that cement boards with asbestos provide a huge advantage in any construction in developing fire protection. But it is also well known, at the same time, that adding asbestos to cement can be harmful and therefore avoided in the building.