Usually, dams are constructed for storing water. Structural engineers are the ones who construct dams. The Structural engineer’s job is to design structures like buildings, bridges, dams, tunnels, etc. Structural engineering is a branch of civil engineering, its applications, and others. The main aim of structural engineers is to design and construct structures that are safe and can withstand the elements to which they get exposed. The importance of dams is that they store water in reservoirs and provide water during drought conditions. Structural engineers are specialists in determining the integrity of a building and evaluating the problems by establishing solutions.
The main difference between a structural and civil engineer is that a civil engineer focuses on design whereas a structural engineer is concerned with the type of materials used for construction. They ensure that the materials used for construction can support that particular design.
Table of Contents
What is the Dam?
A Dam is a structure that is built across a river or a stream to store water. Dams are constructed to provide water for human activities, irrigation, and industries.
Purpose of Dam/Uses of Dam
The main purpose of a dam is to store water or liquid borne materials for several reasons such as flood control, water supply for domestic uses, irrigation, energy generation, recreation, or pollution control.
Water Supply
- Dams are built to control the flow of water in rivers. The stored water is released from the reservoir to provide water for wildlife and ecosystems during a drought, and water can also be provided for the irrigation of crops during the same drought.
- Water collected in the reservoirs of the dam can be used to provide a sufficient amount of freshwater to residentials, industries, and mining activities.
Irrigation
Reservoirs provide water for agriculture to retain crops during natural drought.
Know also: what is structural design? Objectives of structural design
Electricity Generation
- Stored water is used to generate electricity in hydroelectric power stations.
- Hydropower is environmentally friendly because it does not cause global warming, pollution, ozone depletion, or acid rain.
- Over 103,800 megawatts of electricity are generated in hydroelectric power stations, which meets 8-12 percent of the Nation’s power requirements.
Flood Control
Dams are constructed earlier mainly to control floods. It prevents the loss of life and property. Flood control dams store floodwaters and then release them into a river or divert the water for other uses.
Water Storage
- Dams are the main source of water storage. They create reservoirs to supply water for industrial, agricultural, and municipal uses.
- Water collected during the rainy season can be stored for use during summer.
Mine Tailings
It helps in the mining and processing of coal and other minerals, protecting the environment.
Debris Control
Debris is the unwanted wastes, broken outs present in water. Dams help to control and collect the debris during floods. They provide environmental protection, by collecting unwanted wastes.
Navigation
Dams provide a stable system of inland river transportation.
Recreation
The Dam provides recreational facilities like boating, skiing, camping, boat launch, and picnic areas.
Types of Dams
Dams are typically classified according to their size and structure
Based on structure
Based on the structure or type of material used, dams are classified into arch-gravity dams, embankment dams, or masonry dams.
Know also: What is irrigation? Types of irrigation
Arch dams
Arch dam, the stability is gained by a combination of gravity action and arch. If the upstream face of the dam is vertical, the entire weight of the structure must be carried to the foundation through gravitation. The distribution of normal hydrostatic pressure between cantilever and arch will depend upon the stiffness of the dam in both horizontal and vertical directions. If the upstream face is sloped, the distribution of hydrostatic pressure is complicated. The safety of an arch dam is depended on the side walls.
There are two types of single-arch dams, namely the constant-angle and the constant-radius dam. In constant radius, the face radius is the same at all elevations of the dam, whereas in constant-angle dams (variable radius dam) the subtended angle is kept constant and the variation in the distance at various levels is taken care of by varying the radii. Similarly, there is a double-curvature or thin-shell dam, which minimizes the amount of concrete required for construction but transfers large loads to the foundation. The multiple-arch dam is a combination of a number of single-arch dams with concrete supporting abutments.
Gravity dams: In a gravity dam, Earth’s gravity pulling down on the mass of the dam applies a force that holds the dam in place. It is very essential to have an impervious foundation for this type of dam. Gravity dams are differentiated as “solid” or “hollow” and generally made of concrete or masonry.
Arch – gravity dams: Arch-gravity dam is the combination of a gravity dam and arch dam for areas with an enormous amount of water but less material availability. The compression of the dam by the water lowers the horizontal force on the dam.
Barrage dam:A barrage dam is a special kind of dam with a number of gates that can be opened or closed to control the water flow.
Embankment Dams
Embankment dams have two main types, rock-fill, and earth-fill dams. These dams depend on their weight to hold back the force of water.
Rock-fill dams: Small dams constructed of gravel, stone, and other durable material across a drainage way with an impervious zone. The impervious zone is upstream face and made of masonry, concrete, steel sheet piles, plastic material. In some cases, clay is utilized as the impervious material the dam is called a composite dam.
Earth-fill dams: Earth-fill dams are also called earthen dams. A rolled-earth dam is completely constructed using one type of material and contains a drain layer to collect seep water. Modern zoned-earth dams comprise filter and drain zones to collect and remove seep water.
Fixed-crest dams: A concrete barrier built across a river is a fixed-crest dam. These are designed and built to maintain depth in the channel for navigation. These channels pose risks to boaters who may travel over them.
Know also: What is structural design? objectives of structural design
Based on size
The size of the dam influences construction, repair, and cost and also affects the potential range of dam and magnitude of environmental disturbances. Based on size dams are classified as follows
Small dams: Both large dams and small dams are built for multiple purposes like hydroelectric power generation, flood control, and water storage. Small dams have the ability to provide benefits without displacing the people in their surroundings.
Non-jurisdictional dams: A dam is non-jurisdictional when it is usually small in size which excludes it from legal regulations. A dam is categorized as jurisdictional or non-jurisdictional based on the jurisdiction. A non-jurisdictional dam is defined as a dam that creates a reservoir with a capacity of 100 acre-feet and a surface area of 20 acres or less and a height of 10 feet or less. A jurisdictional dam as 25 feet or more height and storing more than 15 acre-feet, dams which do not meet these requirements are considered as non-jurisdictional.
Based on the use
Saddle dam: An auxiliary dam built to confine the reservoir created by a primary dam to allow a higher water elevation or to limit the extent of a reservoir is a saddle dam. A reservoir consists of a similar auxiliary structure called a dike to prevent a flood.
Weir: A weir also called an overflow dam is a type of small dam that is used within the channel of a river to create a detention lake for water abstraction purposes.
Check dam: The check dam is a small structure that is constructed to reduce the velocity of water flow and control soil erosion. Instead, a wing dam is a structure that partly resists a waterway and creates a faster channel that resists sediment accumulation.
Dry dam: Dry dam is a flood retarding structure that is designed to control floods. It normally allows water to flow freely except during times of intense flow which causes flooding.
Diversionary dam: As the name indicates it is built to divert a portion of the water flow of a river from its natural course. The water is diverted into a canal for irrigation or hydroelectric power generation.
Underground dam: Underground dams are built to catch out and store groundwater. In some instances, they are also constructed to prevent the flow of saltwater into a freshwater aquifer. There are two types of underground dams: a sub-surface dam and a sand-storage dam. A sub-surface dam is built over an aquifer from a solid impervious layer. They are constructed using various materials like bricks, stones, steel, and concrete. A sand-storage dam is built over a stream and it should be strong to withstand floods.
Tailings dam: An earth-filled embankment dam that is used to store tailings produced during mining activities after extracting valuable elements from the ore is called a tailings dam. There are three types of tailings dam structures, upstream, downstream, and centerline.
Standard Height of a Dam
The height of a dam is the vertical distance from the downstream toe of the dam to the crest. The height of dams which has sloping crest can be determined by a weighted average height above the bed of the watercourse, eliminating spillways. International commission on large dams (ICOLD) defines large dams as higher than 15m and major dams as 150m in height.
- The structures that are less than 40 ft high or impound less than 1000 acre-feet of water are small dams.
- The structures that are 40-100 ft high or impound 1000-50000 acre-feet of water are intermediate dams.
How to measure the height of a dam?
Engineers determine or measure the height of the dam based on 5 scenarios. The following pictures illustrate the correct positions for measuring a dam. The height of the dam falls into one of the following five scenarios:
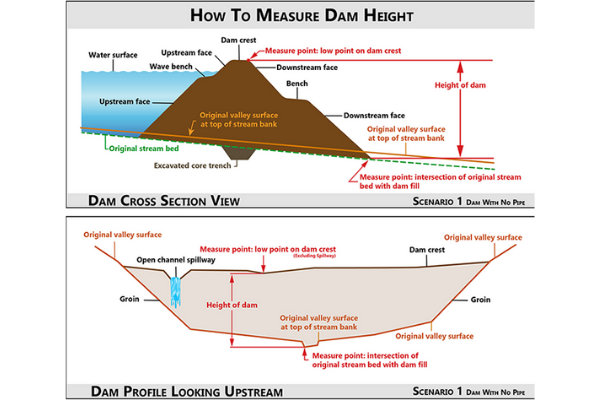
Scenario 1
There is no spillway pipe, drawdown pipe or appurtenant structure exiting embankment close to the toe of the dam. The dam height is measured vertically from the lower point of the crest to the point where the embankment fill intersects the natural stream channel bed.
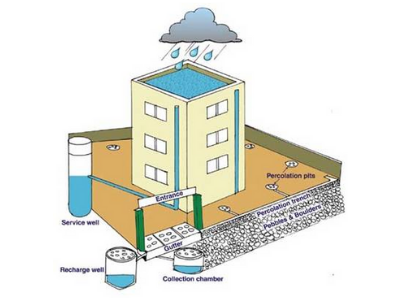
Know also: Rainwater harvesting methods
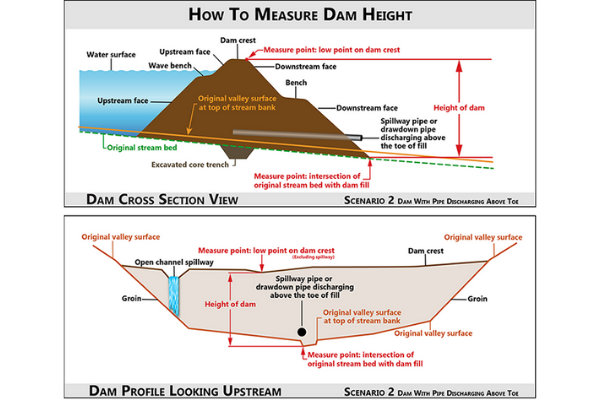
Scenario 2
In this case, the dam has a spillway pipe, drawdown pipe, and other appurtenant structures in the embankment near the toe of the dam, but it is above the natural stream bed. The dam height is measured vertically from the lower point on the crest excluding open channel spillways, to the point of intersection of embankment fill and natural stream bed channel.
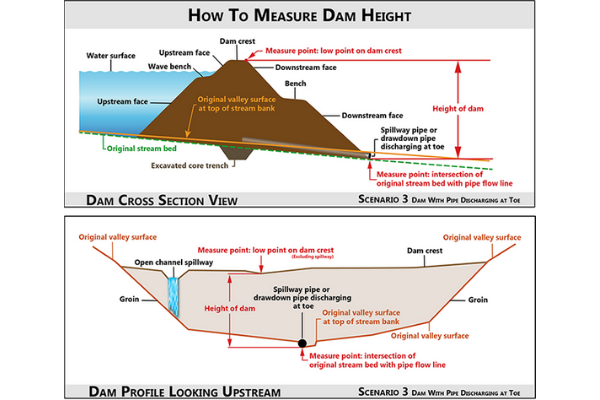
Scenario 3
The dam has a drawdown pipe, spillway pipe and other appurtenant structures exiting the embankment at the point of intersection of the toe of the dam and natural stream bed. The dam height is measured vertically from the crest lower point to the intersection point of the pipe flow line and natural bed stream channel.
Scenario 4
There is no spillway pipe, drawdown pipe or other appurtenant structure exiting the embankment of the dam. The fill has been placed in the valley and the natural stream bed. The height of the dam structure is measured vertically from the lower point on the crest to the intersection point of the valley and stream bed fill which intersects the bed of the natural stream channel.
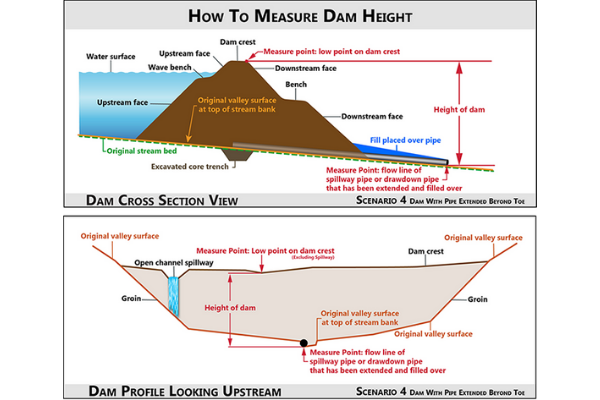
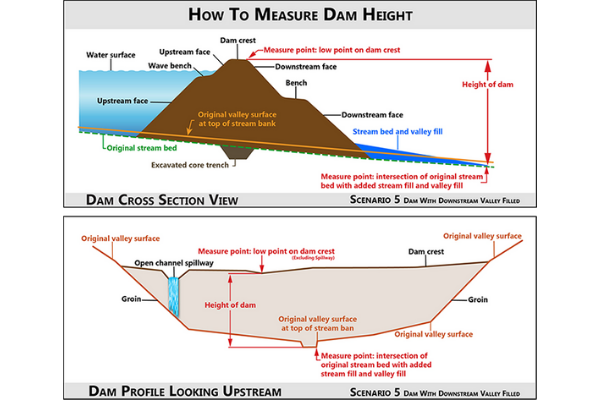
Scenario 5
The dam has a spillway pipe, drawdown pipe, and the appurtenant structure that is extended downstream. The height is measured vertically from the lower point of crest excluding open channel spillways, to the intersection point of the pipe flow line and bed of the natural stream channel. A localized scour hole is not included in the measurement.
Importance of Dams
Dams are considered to be an important source of water. The importance of dams are as follows
- Electricity is generated at a constant rate With the help of hydroelectric power.
- If there is enough electricity and no need for generation, then sluice gates can be closed. Water can be saved for future use when there is a high demand for electricity.
- Dam is designed and constructed by well-qualified structural engineers to span many decades and they also contribute to the generation of power for many years.
- The reservoir behind the dam stores water that can be used for irrigation purposes, recreation, and other forms of activities. Larger dams can also be a tourist attraction.
- The electricity produced by the dams does not release greenhouse gases and they are not harmful to the environment.
Issues in construction and maintenance of Dams
Even though there is much importance of dams, we have few issues also, they are
- Constructing a dam is very expensive.
- It is required to follow the strict guidelines from the government and should maintain a very high standard.
- Many more years are needed to operate to become more profitable enough to compensate for the high building cost.
- People living in nearby areas, villages have chances of flooding.
- Due to flooding they people need to shift to some other places leaving their shelter and farm.
- Large dams cause serious damage to the earth’s surface.
- Water habitats are get affected due to dams.
- Decreases the level of oxygen in the water due to hydroelectric power generation.
Latest innovative technologies for Dam safety
Multipurpose reservoirs play a prominent role in water supply, irrigation, and flood control. In order to ensure the long life and safety of the dams, adaption planning, maintenance, and repair are needed. DAMSAFE is a project sponsored by Dutch partners for the water program and supports decision-making in a long-term approach.
The DAMSAFE consortium comprises the Dutch-based research coordinators and the Dutch companies SkyGeo and Royal Eijkelkamp and the Spanish company iPresas. The main aim of DAMSAFE is to enhance dam safety and water management in India.
Know also: What is a Bridge? Types and main sections
Various technologies, that have been developed for dam safety are
- A risk model that is based on risk-informed Dam safety Assessment estimates existing risk by comparing with international tolerability recommendations, identifies, analyses, and prioritizes risk reduction measures, and evaluates the impact on risk reduction of actions.
- An online monitoring system allows monitoring of the weather, the dam, water quality, and the surface water levels in the reservoir.
- A radar technique called Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PS-InSAR) is used to generate maps of surface deformation with accuracy. Along with dam safety, it provides information on long-term risks and prioritizes operation and maintenance efforts.
- Delft-FEWS is a platform to combine data from various sources and to perform calculations automatically using different numerical models. SOBEK is a suite for hydraulic and morphological simulations, whereas the DAM is a software tool that helps to determine the strength of a dam.
Conclusion
Dams are an important source of water for various means like domestic use, industrial use, and irrigation purposes. They are also into hydroelectric power generation. Dams are constructed to store water in reservoirs for future use. Reservoir water is made to flow through hydraulic turbines to produce electricity. Hydroelectric power is a renewable source of energy because the water that is used to generate power is continuously replenished. Dams play a prominent role during drought as they are the source of stored water. So proper care has to be taken in the construction and maintenance of dams. By including the above dam safety features, you can extend the life of dam structures.