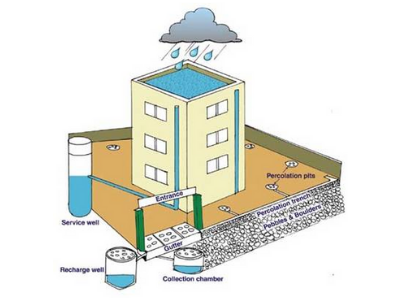
Rainwater harvesting is very important in the current situation as there is scarcity of water. It helps to collect large amounts of water and can reduce the effects of drought. Rainwater can be a primary source of water for many situations and also it is free of chemicals.
Table of Contents
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting is a process of conserving rainwater. Technology is used to collect, store and purify rainwater that runs off from house rooftops, parks, open fields etc…. for future use.
Methods of Rainwater Harvesting
There are mainly two ways of water harvesting, they are; Surface runoff water harvesting and Rooftop rainwater harvesting. It is the collection and storage of rain water for future use, rather than allowing it to flow off. The stored rainwater can be used for various purposes like gardening, irrigation, etc.
1. Surface Runoff Harvesting
Surface runoff harvesting is the collection, storage and treatment of stormwater for its reuse. It can also include other areas from manmade surfaces such as roads, parks, gardens and playing fields. Surface runoff water is an excellent substitute to using mains drinking water for many purposes. If properly planned and designed, Surface runoff catchment systems can accumulate large quantities of rainwater.
The main problem Surface runoff water harvesting poses is the purification process in order to make this water available for reuse. Small reservoirs with bunds are built from soil excavated from within the reservoir to increase its water storage capacity.
2. Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
Rooftop water harvesting is the process through which rain water is collected from the roof catchments and stored. The harvested water is stored in sub-surface ground water reservoir through artificial ground water recharge techniques. This method is very useful and also less expensive. If this is implemented properly, the ground water level can be increased.
Read also: Different types of columns construction
Advantages of Rooftop harvesting
- It provides a self-sufficient water supply.
- The cost of ground water pumping can be reduced.
- Provides chemical free high quality soft water.
- Improves the level of ground water when recharged to the ground.
Components of Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting
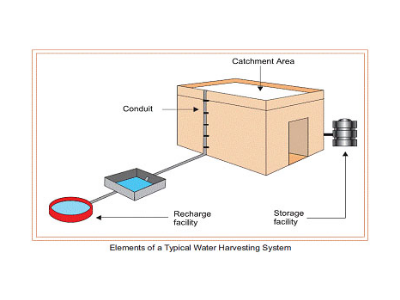
The essential components of the rooftop harvesting method constitutes of the following
1. Catchment
2. Transportation
3. First Flush
4. Filter
Catchment
The catchment of a water harvesting method is the surface area which receives rainwater directly and provides to the system. It may be a courtyard, terrace, paved or unpaved open space. The catchment is the surface area actually provides water to the system.
Transportation
Rainwater from the rooftop has to be carried down to the storage or harvesting system through water pipes or drains. Water pipes should be of required capacity, which are UV resistant. Water from roofs can be collected through gutters and stored in harvesting tanks through pipes. In the catchment area like terrace, the opening of each drain should be covered with a mesh to stop floating materials.
First Flush
The first flush is a valve which ensures that runoff from the first shower of rain is flushed out without entering the system. This is done because the first spell of rain contains the largest amount of pollutants from the air and catchment area.
Filter
The filter is used to take out suspended particles from rainwater collected from the rooftop. There is always some misbelief with reference to roof top rainwater harvesting, that rainwater may contaminate ground water. This may come true if the proper filter mechanism is not used. Filters are used to remove unwanted particles, turbidity and color. After the first flush of rainfall, water will pass through the filters. A filter is a unit filled with fiber, sand and gravel layers to remove impurities from water before it flows into the storage tank.
The filter media has to be cleaned after every rainfall, clogged filter needs to be cleaned frequently as it blocks rainwater from easily flowing into the harvesting tank.
There are various types of filters, but the basic function of all the filters is purification. Different types of filters are
1. Sand, Gravel Filter
Sand, gravel filters are most commonly used filters. These are constructed from bricks and filled with pebbles, gravel and sand. Each layer is separated by wire mesh.
2. Charcoal Filter
A simple charcoal filter can be made in a drum or an earthen pot. The filter is made of sand, gravel and charcoal. Each layer is seperated by a wire mesh and a thin charcoal layer is used to remove the odour.
Read also: Application and importance of viscosity
3. PVC- Pipe Filter
As the name indicates this filter can be made from PVC pipe of 1 to 1.2m length. The diameter of the pipe depends on the rooftop area. The pipe is divided into three divisions by wire mesh. Each division is filled with gravel and sand alternatively and a thin layer of charcoal is also inserted between the layers. Both ends of the filter should have size reduced ends to connect to the inlet and outlet.
4. Sponge Filter
Sponge filter is a simple filter which is made from PVC drum with a layer of sponge in the middle of the drum. It is the cheapest form of filters suitable for residential units.
Methods of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
There are various methods of using rooftop harvesting. They are as follows
1. Storage of Direct Use
In this system, rainwater gathered from the roof of the house is redirected into a storage tank. The storage tank should be designed based on the water requirements and catchment availability. Each pipe should have a mesh at the opening and first flush which is then followed by a filter system before connecting to the tank. Each tank should have a water overflow system.
2. Recharging Groundwater Aquifers
Groundwater can be recharged by various structures to percolate the water into the ground instead of draining away from the surface. Common recharging methods are:
- Recharge of bore wells
- Dug wells recharge
- Recharge pits
- Trench recharging
- Soakaways
- Percolation tanks
Recharge of Bore wells
Rainwater gathered from the rooftop is redirected through pipes to filtration tank. After that filtered water is drained to bore wells to recharge aquifers. Optimum capacity of the tank can be designed based on the area of catchment, rainfall intensity and recharge rate.
Recharge Pits
These are small pits of any shape constructed with brick or stone masonry wall with holes at regular intervals. The pit is covered with perforated covers. The pit should be filled with filter media. These pits are perfect for recharging shallow aquifers.
Dug well
Recharge Dug wells are used as recharge structures. Rainwater from the rooftop is directed to drill wells. The dug well should be cleaned and desalted regularly to improve the recharge rate.
Read also: What is irrigation and types of irrigation?
Trench Recharging
The trench is provided where upper layer of soil is shallow. The trench is filled with porous media like pebbles, brickbats etc..It is made particularly for surface runoff water harvesting. This method is suitable for playgrounds, small houses and drains.
Percolation Tank
These are artificially created tanks which can be built on big campuses. The stored water can be used for gardening and other purposes. Percolation tanks can be built in open spaces, gardens etc.
Advantages
- cost-effective
- Reduces water bill
- Demand for water is decreased
- Improves water and energy conservation
- The quality and quantity of groundwater improved
- Reduces soil erosion, flooding and pollution of surface water
- Excellent source of water for irrigation
Disadvantages
- Requires regular maintenance
- Technical skills are required for installation
- If not properly installed, it may attract mosquitoes
Conclusion
Conserving rainwater is very important in present water crisis situation. So rainwater harvesting helps not only to meet the water demand but also helps to improve the ground water levels. It is good to implement this water harvesting methos wherever possible.




[…] and property. Flood control dams store floodwaters and then release them into a river or divert the water for other […]